Druid 31 Preview: Changing the Segment Sort Order
Up until Druid 30, data in a Druid segment was always sorted by time. But this is about to change. Druid 31 comes with an experimental option to change the segment sort order. With Druid Summit 2024 and the announcement of Druid 31 around the corner, let’s take a look at this new feature.
This blog is based on the public documentation of this pull request.
This is a sneak peek into Druid 31 functionality. In order to use the new functions, you can (as of the time of writing) build Druid from the Druid 31 branch:
git clone https://github.com/apache/druid.git
cd druid
git checkout 31.0.0
mvn clean install -Pdist -DskipTests
Then follow the instructions to locate and install the tarball.
Disclaimer: This tutorial uses undocumented functionality and unreleased code. This blog is neither endorsed by Imply nor by the Apache Druid PMC. It merely collects the results of personal experiments. The features described here might, in the final release, work differently, or not at all. In addition, the entire build, or execution, may fail. Your mileage may vary.
Motivation
Why would you want to change the segment sort order? This is mainly about data compression. Druid can compress data much better if blocks of contiguous rows have the same value in a column. It is also consistent with the tendency to better organize data within Druid.
For instance, range partitioning of data is now becoming the gold standard for batch ingestion. In fact, Imply’s Polaris service offers range partitioning for both batch and streaming ingestion. (This is done by ingesting data into dynamic partitions first and running a preconfigured autocompaction job in the background that makes sure all data is partitioned according to the configured settings. You can do this in open source Druid too, but you have to configure it yourself.) In most cases, if you decide to partition your data by a set of columns, it would also make sense to order them by the same criteria.
This is currently an experimental feature and not all query types are guaranteed to work with alternative segment sort order. Also not that segments written with alternative sort order cannot be processed by older Druid versions.
Lab
With that said, let’s try it out!
Follow the SQL ingestion tutorial until step 5 where you have a query window with an ingestion query. In order to make this a minimal example, remove from the query all columns but __time, channel, and page. Your query should look like this:
REPLACE INTO "wikipedia-time" OVERWRITE ALL
WITH "ext" AS (
SELECT *
FROM TABLE(
EXTERN(
'{"type":"http","uris":["https://druid.apache.org/data/wikipedia.json.gz"]}',
'{"type":"json"}'
)
) EXTEND ("isRobot" VARCHAR, "channel" VARCHAR, "timestamp" VARCHAR, "flags" VARCHAR, "isUnpatrolled" VARCHAR, "page" VARCHAR, "diffUrl" VARCHAR, "added" BIGINT, "comment" VARCHAR, "commentLength" BIGINT, "isNew" VARCHAR, "isMinor" VARCHAR, "delta" BIGINT, "isAnonymous" VARCHAR, "user" VARCHAR, "deltaBucket" BIGINT, "deleted" BIGINT, "namespace" VARCHAR, "cityName" VARCHAR, "countryName" VARCHAR, "regionIsoCode" VARCHAR, "metroCode" BIGINT, "countryIsoCode" VARCHAR, "regionName" VARCHAR)
)
SELECT
TIME_PARSE("timestamp") AS "__time",
"channel",
"page"
FROM "ext"
PARTITIONED BY DAY
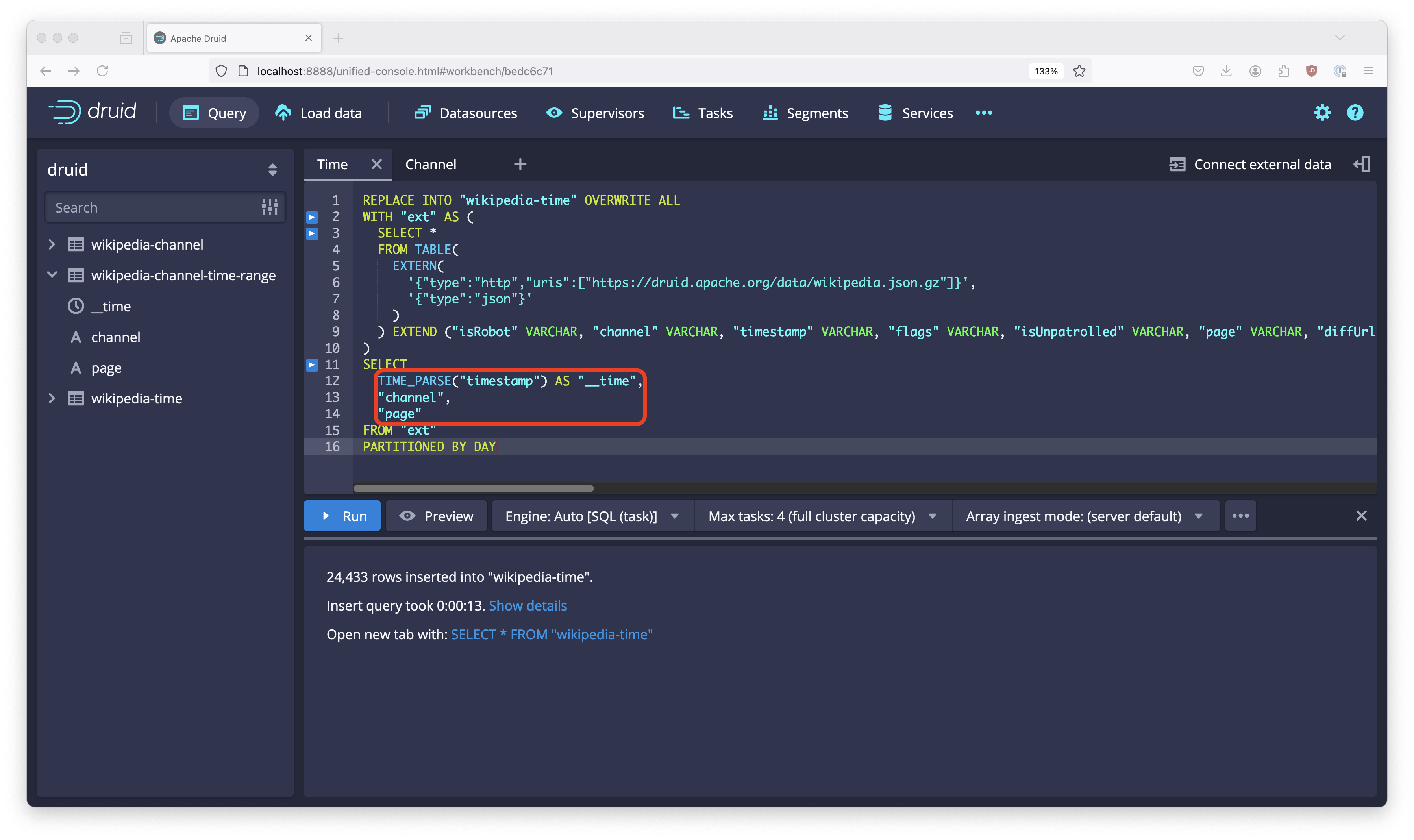
Run this query to get the reference table.
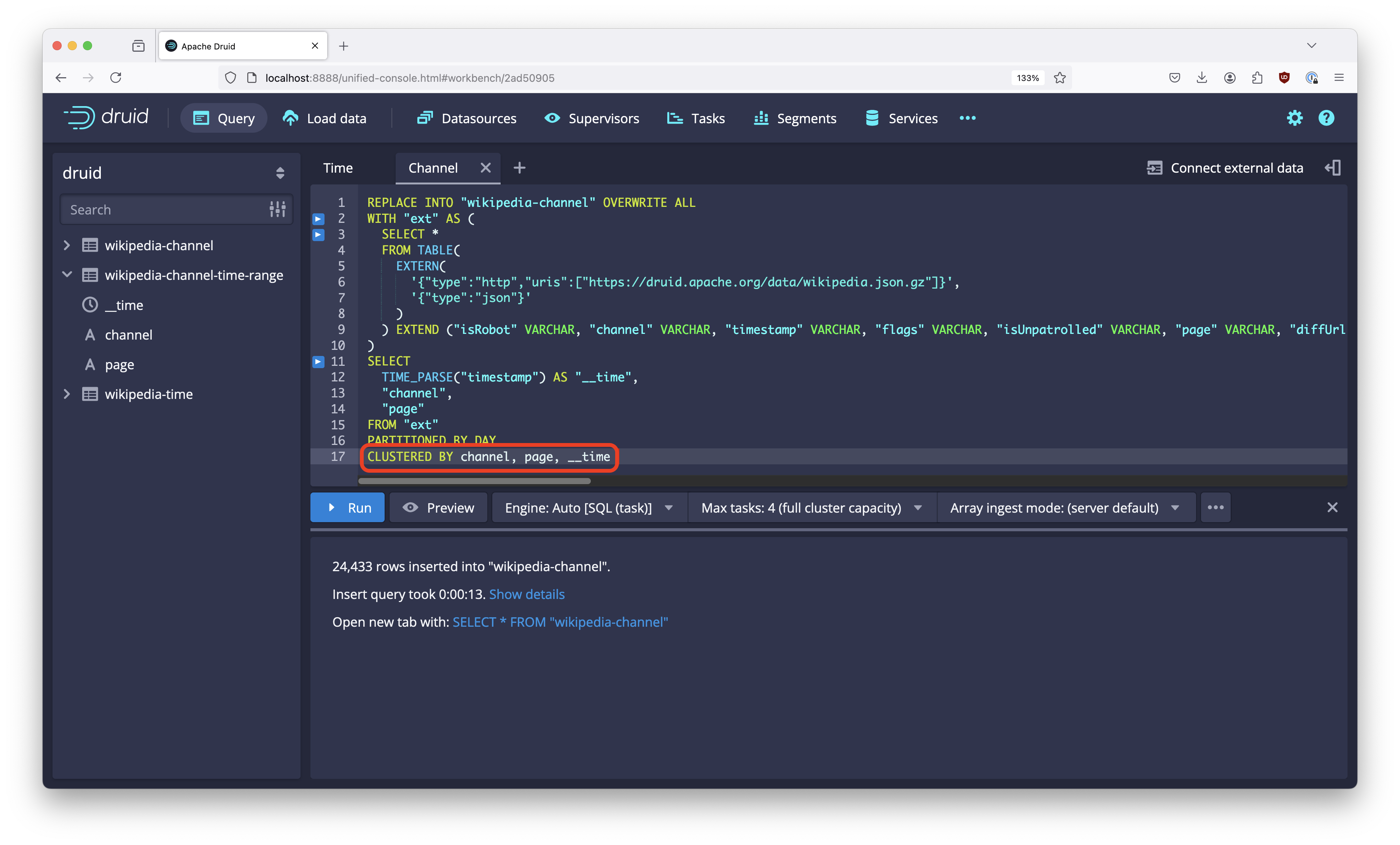
We are now going to sort by channel instead of time first. Because channel is relatively low cardinality, this should make the resulting table smaller.
Sort order in SQL based ingestion is controlled by the CLUSTERED BY clause, which also (and primarily) is used for secondary partitioning. So the next step will be to add a clustering clause to the ingestion query.
Duplicate the query tab to create a copy of the query. In the copy, change the table name from wikipedia-time to wikipedia-channel and add a clustering clause CLUSTERED BY channel, page, __time:
The next thing we need is to enable alternative sort order in the query context. Open the query context from the Engine menu:
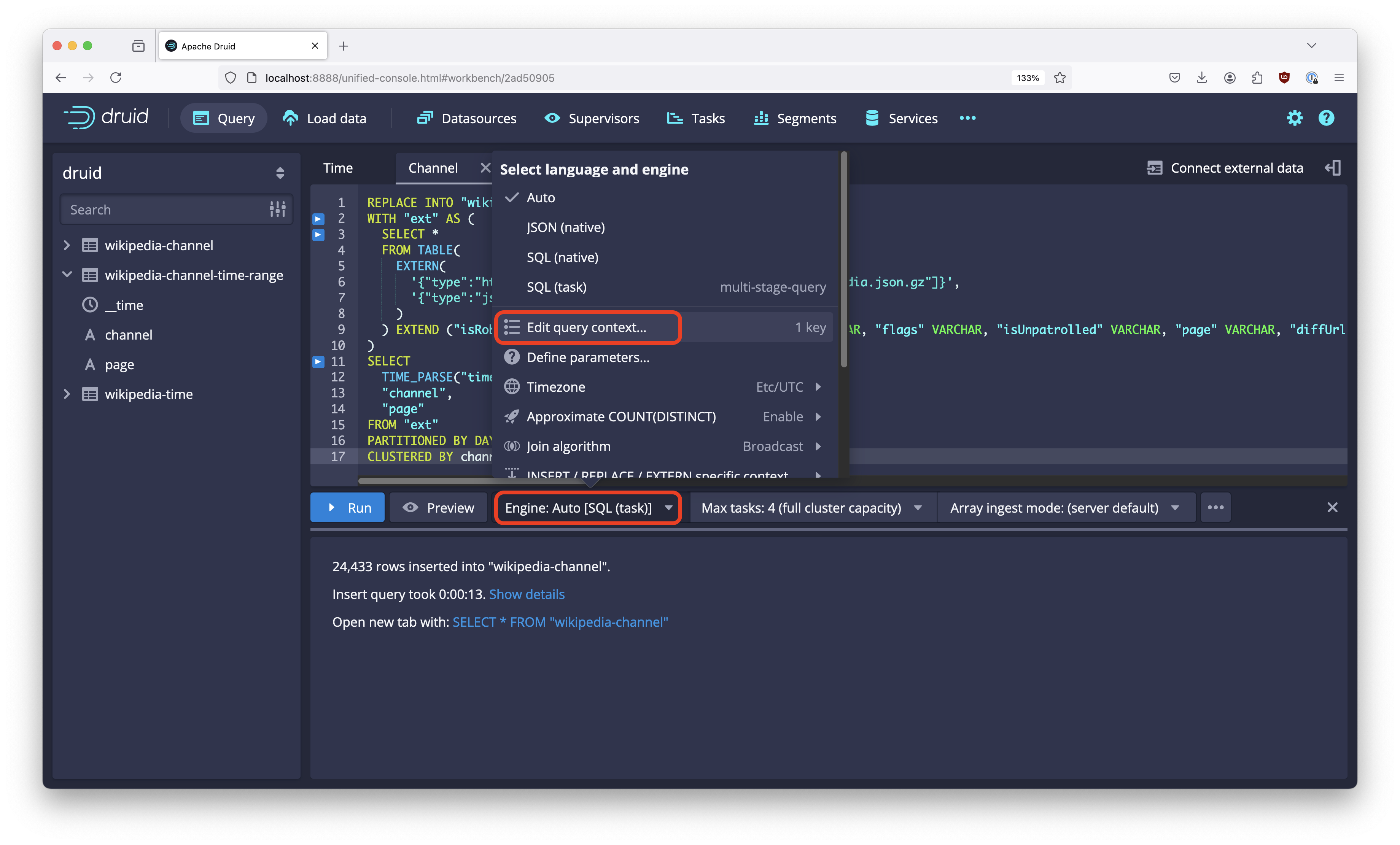
And in the editor window that opens, enter
{
"forceSegmentSortByTime": false
}
and hit Save. Then run this ingestion query, too.
Let’s look at the result:
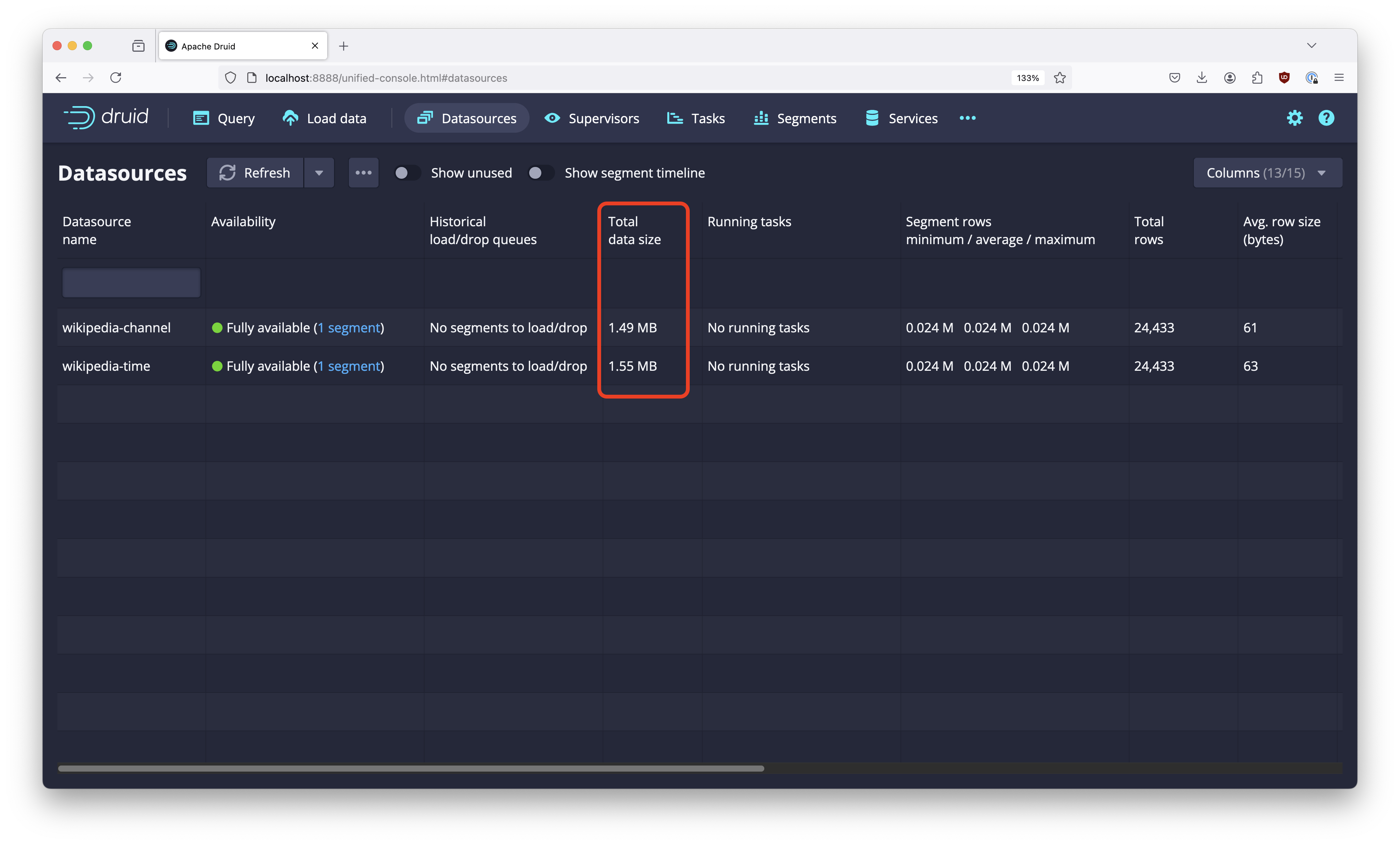
The table that got sorted by channel first is about 4 percent smaller!
In a real life scenario, you could expect even greater space savings.
Conclusion
- Starting with Druid 31, you can sort segments by a column other than the primary timestamp.
- This is still experimental and is enabled by a context flag.
- With alternative segment sorting enabled, the sort order in SQL ingestion is governed by the
CLUSTERED BYclause.